ModCS.Rect
The ModCS.Rect class represents Rects. They are a collection of pixel coordinates on a Surface which represent a part of the surface. They are mostly used for displaying different sprites from a spritesheet.
A ModCS.Rect is userdata. You may access and edit the following values from it:
| Value | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
left |
Number (Casted to integer) | X coordinate of the upper-left corner of the Rect. |
top |
Number (Casted to integer) | Y coordinate of the upper-left corner of the Rect. |
right |
Number (Casted to integer) | X coordinate of the down-right corner of the Rect. |
bottom |
Number (Casted to integer) | Y coordinate of the down-right corner of the Rect. |
Rect Example
This example shows you how to get the Rect of the number 4 sprite from TextBox.bmp
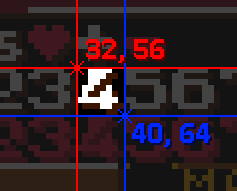
The coordinates of the upper-left corner are 32, 56. The coordinates of the down-right corner are 40, 64. Therefore, the Rect of the number 4 sprite is:
{
left = 32,
top = 56,
right = 40,
bottom = 64
}
ModCS.Rect.Create()
ModCS.Rect.Create(left, top, right, bottom)
Returns a ModCS.Rect.
All parameters are optional. If any parameters are given, the returned ModCS.Rect will use those parameters as Rect values.
ModCS.Rect.Set()
ModCS.Rect.Set(rect, left, top, right, bottom)
Sets the ModCS.Rect given in the rect parameter to a ModCS.Rect with the following parameters.
ModCS.Rect.Put()
ModCS.Rect.Put(rect, x, y, surface, alpha)
ModCS.Rect.Put(rect, x, y, surface, surfaceto)
Draw the given Rect from the surface with ID surface to the screen with coordinates x and y.
The alpha parameter is optional and is a Boolean. If set to false the game will draw the rect without removing any fully black pixels. The default value is true.
The surfaceto parameter is optional and is a number. If set the game will draw the rect to the surface with ID surfaceto.
Note
For a more traditional PutBitmap usage you may use ModCS.Rect.PutEx().
ModCS.Rect.PutEx()
ModCS.Rect.PutEx(rect, viewrect, x, y, surface, alpha)
The same as ModCS.Rect.Put() but with a viewrect which limits the view.